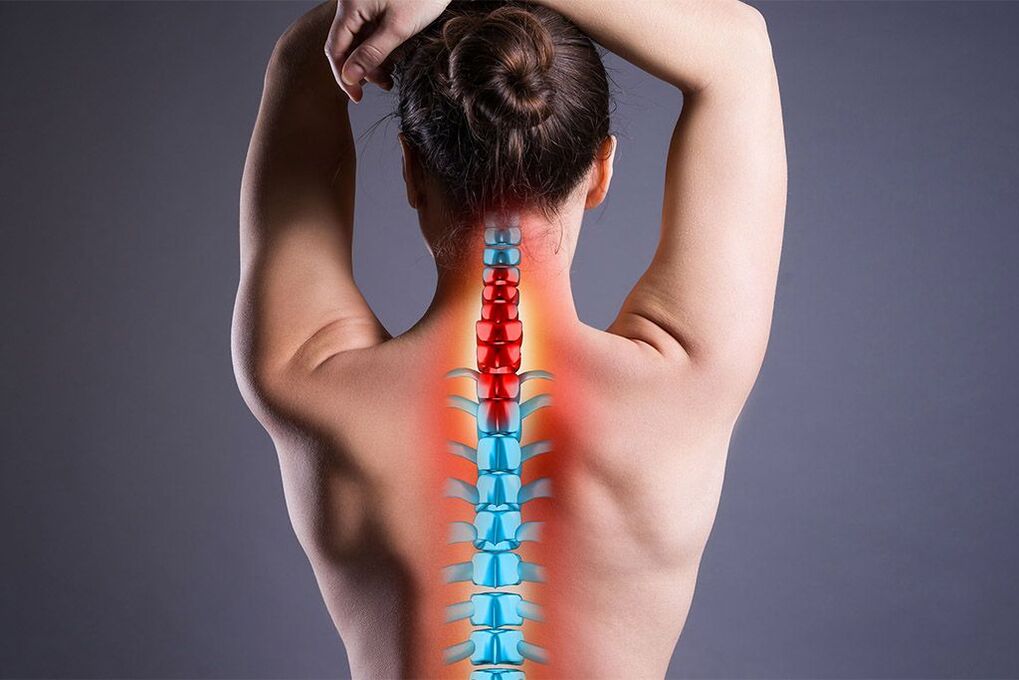
As a result of human walking, the spine, as an axial structure, received the main load. That is why degenerative and dystrophic processes are quite common consequences of human life. One of the most common diseases of the musculoskeletal system is osteochondrosis, which causes severe discomfort and can lead to disability. This article will discuss the most severe form of this pathology - ordinary osteochondrosis.
general characteristics
Osteochondrosis is a degenerative disease of the spine, which most often affects the thoracic, lumbar and cervical regions. This pathology has a direct correlation with age. The disease is much more common in people over 40, but recently there is a tendency towards rejuvenation. Common osteochondrosis differs in that it affects more than one section of a department or several departments at the same time. Due to the progressive development of degenerative processes not only in the bone tissue, but also in the ligamentous apparatus of the spine, the vertebrae become mobile and put pressure on the nerves and blood vessels. Symptoms of ordinary osteochondrosis are associated with this, but it is worth noting that the disease can be asymptomatic for some time.
Important! The pathology requires multidisciplinary control, as it affects not only the musculoskeletal system, but also the nervous system, as well as the internal organs. In addition to the spine itself, the pathological process can also affect other elements of the skeleton.
Etiology and pathogenesis
There are many reasons for widespread osteochondrosis. Some of them are associated with congenital skeletal defects, others with inadequate load during vigorous activity. Particularly common factors that contribute to the development of the clinical picture are:
- injuries;
- flat feet;
- crooked leg - foot deformity (equinovarus, varus, valgus, depending on the position of the heel);
- work related to heavy lifting;
- playing sports without warming up or warming up the muscles;
- work at low temperatures.
Low temperatures are considered provoking factors, since the cold temporarily changes the molecular structure of soft tissues, reduces the intensity of blood circulation, reduces the conduction of nerve impulses and metabolism, and consequently the functioning of the immune system. Other reasons disrupt the biomechanics of the spine and contribute to rapid wear of the intervertebral discs.
Pain in widespread osteochondrosis can be a consequence of osteophytes or disc deformation. The pain is usually radicular, d. m. th. associated with posterior nerve root compression.
Common osteochondrosis easily imitates other diseases. With damage to the chest region, pain appears in the heart area and is mistaken for ischemic processes, and with damage to the lumbar regions - for radiculitis.
Symptoms
Clinical manifestations will depend on which parts are affected and in what combination.
When the cervical spine is affected, the following are characteristic:
- unstable blood pressure;
- headache;
- lack of coordination;
- pain in hands;
- numbness in the upper body and arms.
For pathology in the chest region:
- intercostal neuralgia;
- stiffness in arms and neck;
- dysfunction of internal organs.
If the midsection is affected:
- burning;
- urinary disorders;
- spasms;
- pain while walking.
Based on the above, it is easy to conclude that the pathology affects not only the spine and large joints, but also the autonomic nervous system. The latter is associated with interruptions in the functioning of internal organs. Common polysegmental osteochondrosis can sometimes worsen. In such cases, the manifestations are much more intense. With a combination of disorders of several departments, the symptoms will be corresponding.
Complications
Osteochondrosis can be conditionally divided into moderate osteochondrosis, which is a natural process of wear and tear of the spine as a result of life activities, and severe osteochondrosis, which is most often characterized by complications.
Moderate osteochondrosis is easily treated with conservative treatment. And if it is impossible to completely stop the inevitable aging process, then it is quite possible to significantly slow it down. Complications that severe osteochondrosis can lead to are as follows.
- Spondyloarthrosis.
- Degeneration of the intervertebral disc.
- Spinal stenosis.
Important! Intervertebral discs act as shock absorbers and reduce friction between the vertebrae. Degenerative processes in these structures can lead to protrusion of the nucleus pulposus of the disc and intervertebral herniation. Stretching leads to root compression and pain.
Spondyloarthrosis is degeneration of the facet joints that connect adjacent vertebrae. In another way, such joints are called fascial joints. When the articular cartilage is damaged, painful contact occurs between the vertebrae. With the degeneration of the facial joints, bone growths appear more often, which leads to spondylosis.
Stenosis is a narrowing (in this case, of the spinal canal). Typically, stenosis is the result of pathologies such as intervertebral hernia or spondylosis. Bony growths and hernial protrusions compress nerve roots at their entry and exit points.
The clinical picture of severe osteochondrosis is the result of complications:
- chronic back pain;
- friction of bone surfaces;
- stiffness;
- sudden muscle weakness;
- decreased reflexes;
- tingling sensation in limbs;
- radiation pain;
- sciatica symptoms.
Sciatica is caused by compression of the sciatic nerve.
Distribution
There are four degrees of osteochondrosis. The classification is done on the basis of the collected history and with the help of instrumental diagnostic methods. The main criteria in this classification are pain and neurological symptoms.
- Grade I - pain is easily relieved with medication.
- Grade II - characterized by prolonged pain and spinal deformities with moderate neurological symptoms.
- Grade III - pain is systemic, neurological symptoms are significant.
- Grade IV - constant pain, multiple neurological deficits. Disorder in the conduction of nerve impulses. Paralysis and paresis.
In case of widespread dysplastic osteochondrosis, the patient is assigned the status of disability. Depending on the general condition of the patient, the degree and intensity of the development of the clinical picture, disability can be divided into three groups.
Types of disability in osteochondrosis.
| GROUP | Description |
|---|---|
| First group | The functions of the spine are lost. The patient is unable to move independently and take care of himself. |
| Second group | The patient is able to move and perform small tasks, but periods of irritation are frequent. The operation is contraindicated or useless for any reason. Or the operation has already been performed, but it was ineffective. |
| The third group | The patient is capable of self-care. There is pain and vestibular symptoms, but the frequency of irritation is moderate and periodic. |
The disability group is assigned by the doctor on the basis of several studies to assess the ability to work.
Diagnosing
When you visit a doctor, the diagnosis will consist of several components. The first and most important is the collection of anamnesis based on the subjective information provided by the patient. Attention is paid to family history, as osteochondrosis has a genetic component. The specialist asks about the workplace, living conditions and the course of the disease itself, and the patient must describe exactly what is bothering him. The best results can be achieved with good feedback between the patient and the doctor.
The other method is an objective study, which is carried out by a specialist himself or using instrumental methods. The doctor checks the range of motion of the neck and limbs, which may be significantly reduced due to pain and stiffness. Using the palpation method, he records how many muscles are spasming and how curved the spine is. Attention is drawn to a neurological examination, with the help of which weakened reflexes can be traced. This symptom can be the result of compression or damage to the nerve.
Instrumental methods for diagnosing common osteochondrosis include:
- X-ray of the entire spine in two projections.
- MRI to evaluate ligaments and nerve tissue.
- An electrophysiological study to test the conduction of nerve impulses.
X-rays are effective for determining the presence of bone growths - osteophytes, narrowing of the spinal canal and the presence of other diseases that are a consequence of osteochondrosis, for example, scoliosis.
Computed tomography can also be used in conjunction with MRI. Using a CT scan, you can determine the degree of nerve compression from the stimuli.
The diagnosis of widespread polysegmental osteochondrosis is made if other pathologies that cause the destruction of vertebrae (for example, tuberculosis) have been excluded and if several segments of one or more departments are affected.
There are additional diagnostic methods. This includes:
- Bone scan.
- Discography.
- Myelogram.
A bone scan can detect conditions such as osteoarthritis, fractures or infections. This method is radionuclide and is suitable for differential diagnosis and for determining possible complications.
During discography, a contrast agent is injected into the nucleus pulposus of the intervertebral disc. This method is effective in determining the presence of a disc herniation.
Myelogram is also a contrast research method. Contrast is injected into the spinal canal and a picture is taken using X-rays or CT. Using this method, you can determine the condition of the spinal cord, the presence of narrowings and compressions.
Treatment
Treatment is based on the following mechanisms.
- Slowing down the degenerative process by improving the supply of nutrients to the structures of the musculoskeletal system.
- Stabilization of the spine.
- Elimination of compressed nerve fibers.
- Relief of symptoms.
The following drugs are used for drug treatment:
- non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs that relieve inflammation and pain;
- Anilides relieve pain in the initial stages;
- local analgesics in the form of ointments;
- muscle relaxants to reduce muscle spasm and increase range of motion;
- B vitamins to improve the conductivity of nerve tissue;
- chondroprotectors, which reduce the rate of progression of degenerative processes by integrating active substances (condoitin sulfate and glucosamine) into cartilage cells. As a result, metabolism is normalized and clinical manifestations are reduced. The drug has been used for a long time and requires special consultation during pregnancy, lactation and the presence of gastrointestinal diseases. An absolute contraindication is phenylketonuria;
- antispasmodics relieve smooth muscle spasms and thus relieve the manifestations of osteochondrosis in the internal organs;
- antioxidants;
- antidepressants to eliminate the psychosomatic component of this disease. They interfere with the transmission of nerve impulses from the central nervous system to the brain. Promote the production of endorphins and help solve the problem of chronic insomnia due to constant pain.
- neuropathic agents to eliminate damage to nerve endings.
- opiates for excruciating pain and ineffectiveness of other pain relievers.
The following are used as invasive medical procedures:
- injection of steroids into the epidural space. Steroids are powerful anti-inflammatory drugs. They relieve inflammation of the nerve roots, which helps relieve pain caused by radiculopathy. Complicated procedure. It requires a qualified specialist;
- facial joint injections. Injected drugs lead to local numbness and pain relief.
It is important to know! Taking medications is not intended to get rid of the disease - there are no drugs that can completely eliminate osteochondrosis, which is a chronic disease. Medicines are prescribed only to relieve symptoms.
Medicines are prescribed by the attending physician. The patient is informed about the possible side effects of each drug and then decides for himself which course of treatment to choose.
For symptoms that give reason to suspect osteochondrosis, contact a vertebrologist, orthopedist and neurologist. Quality medical care will consist of close cooperation between these specialists with each other and with the patient.
Physiotherapy
Physiotherapy is used as a group of auxiliary therapeutic measures to improve blood circulation and metabolism in the affected tissue. For widespread osteochondrosis, the following methods are used.
- Electrophoresis (based on the movement of colloidal particles under the influence of an external electric field).
- Phonophoresis (a combination of ultrasound and medication).
- Magnetotherapy (using a static magnetic field).
- UHF therapy (ultra high frequency therapy).
- Electrostimulation (stimulation of nerves and muscles).
- Acupuncture (acupuncture).
- Laser exposure.
In addition to physiotherapy, manual therapy and physical therapy are actively used. Professional massage can lead to long-term remission. Therapeutic exercises should not be performed during an exacerbation of the disease, as this can lead to complications. During the remission period, moderate physical activity maintains muscle tone, and thus the spine. The exercises are performed under the supervision of an instructor and are prescribed by the attending physician.
During an irritation, you cannot warm the spine, but you can wear a corset, but only for a few hours. In other cases, wearing a corset for more than a few hours is not optimal because it can lead to muscle atrophy.
Manual therapy can increase clearance of pinched nerves and reduce neurological symptoms. Alternative methods are leeches and vacuum massage. These methods are aimed at improving blood circulation in the affected area. The sanitary spa treatment is beneficial. Special preference is given to water procedures.
Surgery
During the treatment of osteochondrosis, specialists are more willing to resort to conservative therapy, however, for the proper effect, a lot of time, patience and scrupulous adherence to the patient's recommendations are required. If conservative treatment is ineffective, only then should you resort to invasive methods. Usually the operation is palliative. This means that the operation will be performed only to relieve the symptoms and relatively improve the quality of life, but not for a complete cure (it is fair to say that even conservative treatment does not lead to the complete elimination of the disease, butthe patient's acceptability to non-invasive therapy is a sign of a good prognosis).
There are two types of surgery: decompression and stabilization. The first is aimed at relieving nerve compression, and the second is aimed at stabilizing the spine. The following operations are classified as decompression operations.
- Facetectomy – removal of cheek nodes to relieve compression.
- Foraminotomy is an increase in the lumen of the spinal canal, which is narrowed due to osteophytes.
- Laminectomy is the removal of the back part of the vertebra, which can be deformed due to osteochondrosis.
- Laminotomy - removal of a fragment of the back of the vertebra to widen the spinal canal.
These operations require a posterior approach, but in the case of intervertebral hernia, the surgical approach will be anterior.
Anterior approach decompression operations are as follows.
- Discectomy - removal of an intervertebral disc.
- Corpectomy - removal of the entire vertebral body with adjacent discs.
Stabilizing operations include:
- Spinal fusion is a method of fusing the vertebrae.
- Artificial intervertebral disc.
The need for stabilizing operations arises after discectomy.
Operations are rarely prescribed because there is a risk of developing serious complications.
Complications include:
- pain relapses;
- false union;
- infection;
- phlebitis in the limbs;
- violation of the act of urination;
- pain due to transplant;
- failure of embedded connectors.
The postoperative period lasts several months. Stitches heal 2 weeks after surgery. If complications are detected, you should immediately consult a doctor.
After the operation, a rehabilitation course is carried out to speed up the healing process and restore full working capacity.
General recommendations
Proper nutrition helps prevent the recurrence of the deterioration of common osteochondrosis. Proper nutrition is primarily necessary to maintain a stable body weight, as excess weight causes additional stress on the spine. In this case, the diet should be complete, fortified and rich in calcium, magnesium and potassium. It is necessary to limit the consumption of coffee as it removes calcium from the body. It is useful to visit the pool. You should avoid staying in one position all the time.
If there are frequent exacerbations and a lack of discipline to follow the recommendations exactly, it is better to undergo a full course of treatment in a hospital under the supervision of a doctor.
You cannot take medicine yourself.
Let's sum it up
Often, widespread osteochondrosis develops after incompletely cured "single" osteochondrosis. This fact suggests that if any concern appears, you should immediately contact the doctor, without hoping that the pain will go away by itself. In this case, it will be much easier to prevent the development of other pathologies, and even more so to cure the root cause.































